Circular Economy in Marketing: Shifting Towards Sustainability and Longevity
In today's world, sustainability isn't just a trend—it's a necessity. Businesses are increasingly embracing sustainable practices, and yet the question arises as to whether sustainability is enough. This is where the concept of a circular economy comes in. But what does this mean for marketing? Let's explore how marketing can align with the principles of the circular economy to foster sustainability for people and the planet.
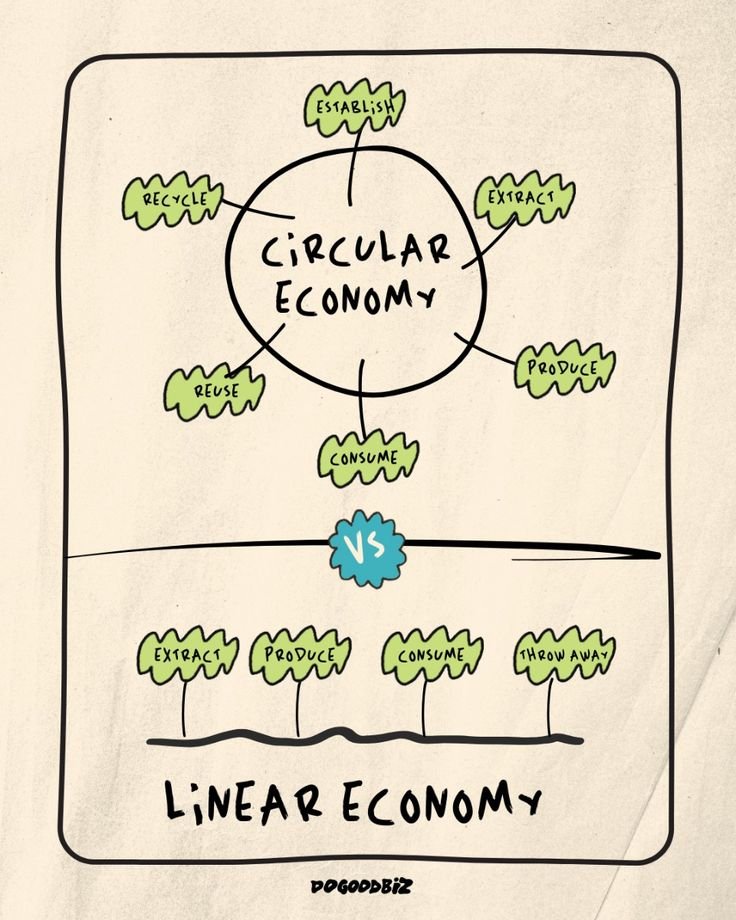
What is Circular Economy?
The concept of circular economy challenges the traditional linear model of production and consumption (take, make, dispose) by prioritizing sustainability and resource efficiency.
At its core, circular economy aims to minimize waste, reduce environmental impact, and maximize the value of products and materials throughout their lifecycle.
In the realm of marketing, we often witness a linear approach where content creation follows a 'use and discard' mentality. This approach leads to the proliferation of content that may not be sustainable or aligned with long-term planetary goals.
How circular economy principles can reshape marketing practices
Designing out Waste: In circular marketing, the focus shifts from creating disposable content to crafting long lasting campaigns that have ongoing value. This involves designing marketing strategies that prioritize quality over quantity, ensuring that every piece of content serves a purpose and contributes to long-term brand goals.
Example: Instead of producing numerous short-lived social media posts that quickly fade from relevance, brands can create evergreen content that remains valuable to their audience over time. This not only reduces the digital footprint associated with content creation but also enhances brand credibility and authority. For tips on strategizing your marketing campaigns beyond short form, ephemeral social media content, read our article here. To learn how to repurpose your content, click here!
Keeping Products and Materials in Use: Circular economy encourages marketers to extend the lifecycle of their content and materials. This can be achieved through strategies such as repurposing, upcycling, and reusing existing content assets. By leveraging existing resources creatively, marketers can minimize waste and maximize the return on their content investments.
Example: Repurposing blog articles into comprehensive guides, transforming social media graphics into printable resources, or compiling video content into educational series can extend the usefulness of content beyond its initial creation.
Regenerating Systems: Marketing in alignment with circular economy principles involves considering the broader impact of promotional activities. This includes using sustainable materials for packaging, opting for digital marketing channels to reduce paper waste, and promoting eco-friendly practices among consumers. Click here to read our article on sustainable content batching.
Example: Implementing digital marketing strategies such as email campaigns and social media promotions not only reduces paper consumption but also allows for targeted audience engagement without relying on physical materials.
Challenges in Current Marketing Practices
Traditional marketing practices have long been criticized for their role in perpetuating waste and overconsumption, contributing to environmental degradation and resource depletion.
Here are some key issues associated with current marketing practices:
Fast Fashion: In the fashion industry, fast fashion epitomizes the throwaway culture promoted by traditional marketing strategies. Brands churn out new collections at breakneck speed, encouraging consumers to buy more frequently and discard clothing after only a few uses. This relentless cycle of production and consumption leads to enormous textile waste and environmental pollution, as fabrics often end up in landfills or incinerators.
Planned Obsolescence: Planned obsolescence is a deliberate strategy employed by marketers to shorten the lifespan of products, thereby compelling consumers to replace them more frequently. This practice not only drives up consumption but also increases electronic waste (e-waste) as outdated gadgets and appliances are discarded in favor of newer models. From smartphones to home appliances, planned obsolescence undermines sustainability by prioritizing profit margins over product durability.
Excessive Packaging: Packaging plays a crucial role in marketing, serving as a tool to attract consumers and communicate brand identity. However, excessive and non-recyclable packaging contributes significantly to waste generation. Single-use plastics, elaborate cardboard boxes, and non-biodegradable materials often accompany products, adding to landfill volumes and posing environmental hazards.
Disposable Marketing Content: In the digital age, marketing content is often produced in large volumes to cater to fleeting trends and short attention spans. Social media posts, email campaigns, and digital advertisements are created rapidly, aiming for immediate impact but often lacking longevity or sustainability. This disposable approach to content creation leads to a constant demand for new material, driving up resource consumption and energy usage associated with digital infrastructure.
Shifting Towards Circular Marketing
Addressing these challenges requires a paradigm shift towards sustainable marketing practices that prioritize longevity, resource efficiency, and planetary stewardship. Adopting circular economy principles in marketing can mitigate these issues by promoting durability, reusability, and responsible consumption.
Here are some actionable ways you can begin to put into practice to help you adopt a more circular approach to marketing:
Content Strategies: Incorporating circular economy principles into content strategies can involve creating educational and informative content that is timeless, helping it to be relevant now and into the future. Emphasize creating evergreen content that remains relevant and valuable over time. Evergreen content addresses timeless topics and provides enduring solutions or insights that can be useful for readers regardless of when they encounter it. Another way to implement sustainability into your content strategy is by prioritizing interactive content formats such as quizzes, polls, and interactive infographics to engage your audience actively. These formats not only educate but also encourage participation and sharing, amplifying the reach and impact of your message.
Design Integration: Encourage designers and marketers to collaborate from the outset, ensuring marketing materials are timeless and aligned with the brand's long-term vision. This involves creating visual elements, such as logos, color schemes, and typography, that can withstand changing trends and remain relevant over extended periods. By focusing on longevity, brands reduce the need for frequent redesigns and rebranding efforts, thereby minimizing the negative impact associated with producing new brand materials.
Collaborative Marketing: Collaboration with like-minded brands is a powerful strategy to amplify the impact of circular economy initiatives. Partnering for joint marketing campaigns allows brands to pool resources, share expertise, and reach a broader audience with messages promoting sustainability. Collaborative efforts can showcase innovative solutions, product lifecycle stories, and collective efforts towards reducing waste and promoting reuse.
Loyalty Programs with Sustainable Incentives: Develop loyalty programs that reward customers for sustainable behaviors such as product recycling, referral programs, opting for eco-friendly packaging, or choosing products/services with minimized negative planetary impact. Use marketing channels to promote these incentives and educate customers on their role in supporting circular economy practices.
Virtual Service Delivery Options: Expand virtual service delivery options to reduce the environmental impact of travel and commuting. Offer online consultations, digital service delivery, and virtual workshops to minimize carbon emissions and resource consumption associated with in-person services. Virtual service delivery reduces overhead costs associated with maintaining physical spaces and facilities while reaching a global audience without geographical limitations, making your offers more accessible.
Employee Sustainability Training: Implement training for your team or employees to promote sustainable practices within your business. Educate employees on conservation, waste reduction, and ethical business practices, empowering them to advocate for sustainability initiatives internally and externally.
Embracing circular marketing not only aligns businesses with planetary needs but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust. As marketers, we have a pivotal role in shaping consumer behavior and promoting sustainable practices. By adopting a circular economy approach to marketing, we not only reduce negative planetary impact but also build trust, loyalty, and resilience within our communities. Together, we can create a more sustainable future for generations to come. Have a practice you are ready to implement in your own business based on what you’ve learned? Follow us on Instagram and share your journey with us so that we can celebrate you and your journey to applying circular principles into your marketing practices!
Until next time…
DoGoodBiz Studio - Natalie Brite